Data Integration
- Data Integration
- All Products

VARIANCE(numeric_value[,filter_condition] )
Argument
| Required/
Optional
| Description
|
|---|---|---|
numeric_value
| Required
| Numeric data type. Passes the values for which you want to calculate a variance. You can enter any valid transformation expression.
|
filter_condition
| Optional
| Limits the rows in the search. The filter condition must be a numeric value or evaluate to TRUE, FALSE, or NULL. You can enter any valid transformation expression.
|
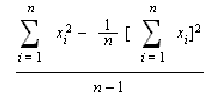
VARIANCE( TOTAL_SALES )
|
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|