Common Content for Data Engineering
- Common Content for Data Engineering 10.5
- All Products

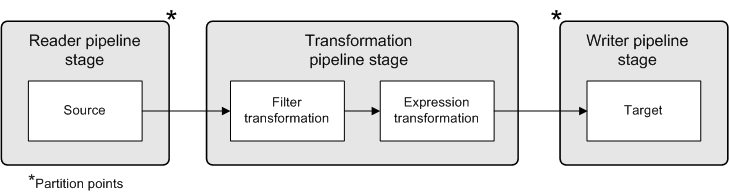
Reader Thread
| Transformation Thread
| Writer Thread
|
|---|---|---|
Row Set 1
| -
| -
|
Row Set 2
| Row Set 1
| -
|
Row Set 3
| Row Set 2
| Row Set 1
|
Row Set 4
| Row Set 3
| Row Set 2
|
Row Set n
| Row Set (n-1)
| Row Set (n-2)
|