Data Engineering Integration
- Data Engineering Integration 10.5
- All Products

|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Property
| Description
|
|---|---|
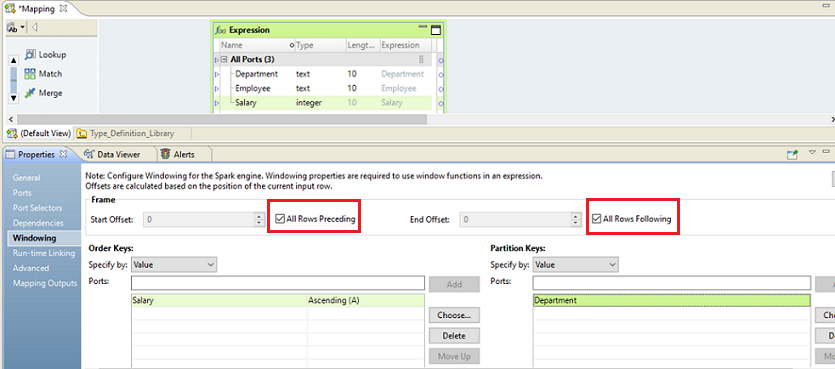
Order key
| Salary Ascending . Arranges the data by increasing salary.
|
Partition key
| Department . Groups the rows according to department.
|
Start offset
| All Rows Preceding
|
End offset
| All Rows Following
|
Salary - AVG ( Salary ) = Salary_Diff
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|