Cloud Data Integration for PowerCenter
- Cloud Data Integration for PowerCenter
- All Products

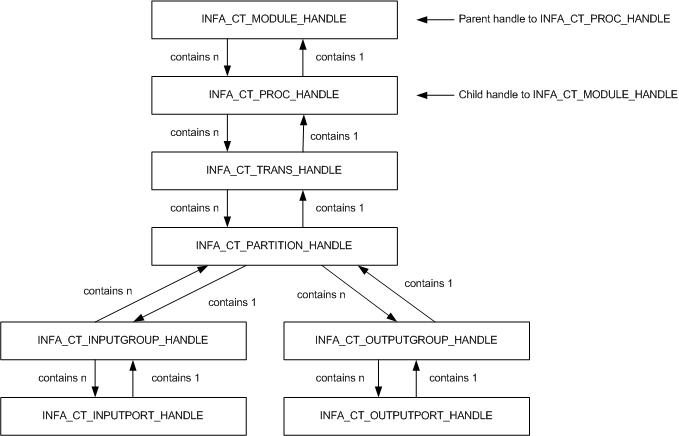
Handle Name
| Description
|
|---|---|
INFA_CT_MODULE_HANDLE | Represents the shared library or DLL. The external procedure can only access the module handle in its own shared library or DLL. It cannot access the module handle in any other shared library or DLL. |
INFA_CT_PROC_HANDLE | Represents a specific procedure within the shared library or DLL. You might use this handle when you need to write a function to affect a procedure referenced by multiple Custom transformations. |
INFA_CT_TRANS_HANDLE | Represents a specific Custom transformation instance in the session. |
INFA_CT_PARTITION_HANDLE | Represents a specific partition in a specific Custom transformation instance. |
INFA_CT_INPUTGROUP_HANDLE | Represents an input group in a partition. |
INFA_CT_INPUTPORT_HANDLE | Represents an input port in an input group in a partition. |
INFA_CT_OUTPUTGROUP_HANDLE | Represents an output group in a partition. |
INFA_CT_OUTPUTPORT_HANDLE | Represents an output port in an output group in a partition. |