Cloud Data Integration for PowerCenter
- Cloud Data Integration for PowerCenter
- All Products

Column
| Datatype
|
|---|---|
AcctID | String |
CustID | Integer |
Balance | Double |
StartDate | Datetime |
EndDate | Datetime |
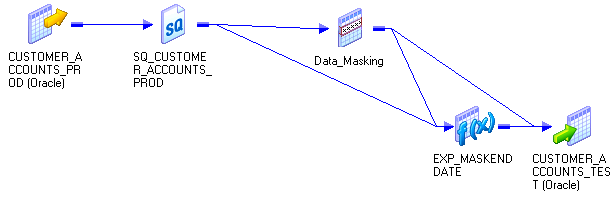
Input Port
| Masking Type
| Masking Rules
| Description
| Output Destination
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
AcctID | Random | Mask format AA+DDDDD Result String Replacement Characters ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ | The first two characters are uppercase alphabetic characters. The third character is a dash and is not masked. The last five characters are numbers. | Customer_Account_Test target |
CustID | Key | Seed = 934 | The seed is 934. The CustID mask is deterministic. | Customer_Account_Test target |
Balance | Random | Blurring Percent Low bound = 10 High bound = 10 | The masked balance is within ten percent of the source balance. | Customer_Account_Test target |
Start_Date | Random | Blurring Unit = Year Low Bound = 2 High Bound = 2 | The masked start_date is within two years of the source date. | Customer_Account_Test target Exp_MaskEndDatetransformation |
DIFF = DATE_DIFF(END_DATE,START_DATE,'DD') out_END_DATE = ADD_TO_DATE(out_START_DATE,'DD',DIFF)