Data Engineering Integration
- Data Engineering Integration 10.2.1
- All Products

Property
| Applicable Values
| Description
|
|---|---|---|
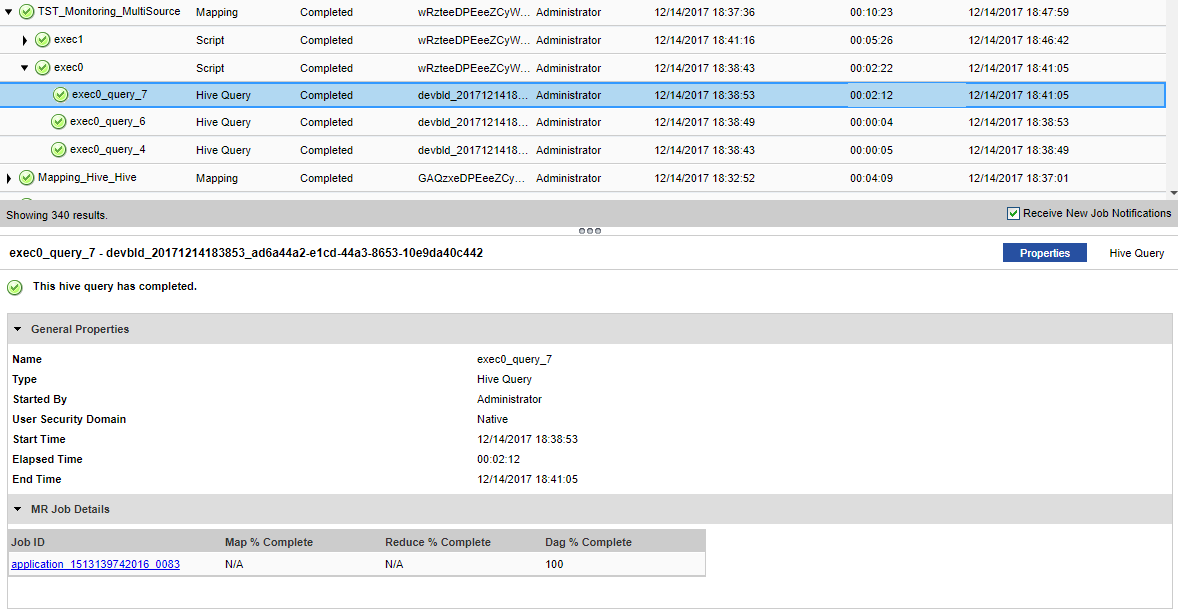
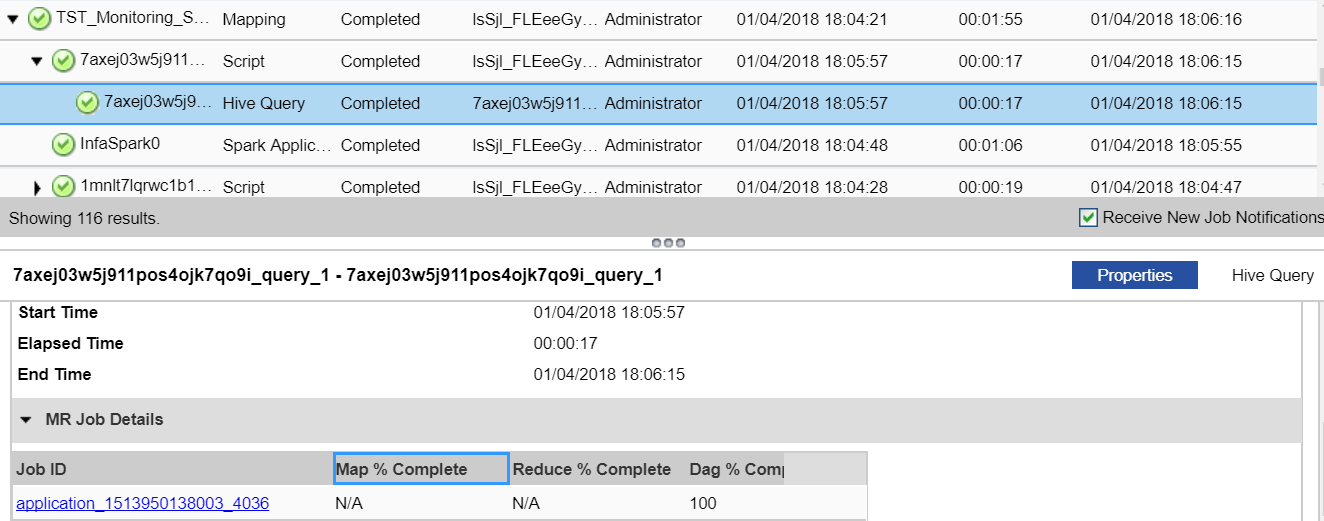
Job ID
| Application_<name>
| You can select the link under Job ID to view the application cluster.
For example, if the Job ID property contains a value starting with the prefix application_ in the MR Job Details pane, the naming convention indicates that the Tez engine is in use.
You can click the link under Job ID to view the application cluster. If you click the Tracking URL for the Tez job, you get redirected to the Hadoop Resource Manager. If you then click History, you can view the Tez view, which is provided by the Hadoop distribution in Ambari.
For each application ID, there are multiple DAGs information.
|
Map % Complete
| N/A
| Map % is not applicable for Tez.
|
Reduce % Complete
| N/A
| Reduce % is not applicable for Tez.
|
DAG % Complete
| 0 - 100
| You can specify a value from 0 through 100 for Tez.
|