PowerCenter
- PowerCenter 10.4.0
- All Products

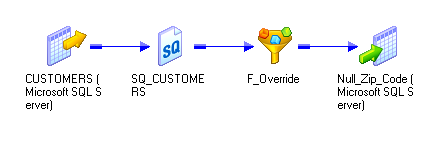
SELECT CUSTOMERS.CUSTOMER_ID, CUSTOMERS.COMPANY, CUSTOMERS.FIRST_NAME, CUSTOMERS.LAST_NAME, CUSTOMERS.ADDRESS1, CUSTOMERS.ADDRESS2, CUSTOMERS.CITY, CUSTOMERS.STATE, CUSTOMERS.POSTAL_CODE, CUSTOMERS.PHONE, CUSTOMERS.EMAIL FROM CUSTOMERS WHERE CUSTOMERS.LAST_NAME LIKE 'John%' OR CUSTOMERS.LAST_NAME LIKE 'Jon%'
CREATE VIEW PM_V4RZRW5GWCKUEWH35RKDMDPRNXI (CUSTOMER_ID, COMPANY, FIRST_NAME, LAST_NAME, ADDRESS1, ADDRESS2, CITY, STATE, POSTAL_CODE, PHONE, EMAIL) AS SELECT CUSTOMERS.CUSTOMER_ID, CUSTOMERS.COMPANY, CUSTOMERS.FIRST_NAME, CUSTOMERS.LAST_NAME, CUSTOMERS.ADDRESS1, CUSTOMERS.ADDRESS2, CUSTOMERS.CITY, CUSTOMERS.STATE, CUSTOMERS.POSTAL_CODE, CUSTOMERS.PHONE, CUSTOMERS.EMAIL FROM CUSTOMERS WHERE CUSTOMERS.LAST_NAME LIKE 'John%' OR CUSTOMERS.LAST_NAME LIKE 'Jon%'
SELECT PM_V4RZRW5GWCKUEWH35RKDMDPRNXI.CUSTOMER_ID, PM_V4RZRW5GWCKUEWH35RKDMDPRNXI.COMPANY, PM_V4RZRW5GWCKUEWH35RKDMDPRNXI.FIRST_NAME, PM_V4RZRW5GWCKUEWH35RKDMDPRNXI.LAST_NAME, PM_V4RZRW5GWCKUEWH35RKDMDPRNXI.ADDRESS1, PM_V4RZRW5GWCKUEWH35RKDMDPRNXI.ADDRESS2, PM_V4RZRW5GWCKUEWH35RKDMDPRNXI.CITY, PM_V4RZRW5GWCKUEWH35RKDMDPRNXI.STATE, PM_V4RZRW5GWCKUEWH35RKDMDPRNXI.POSTAL_CODE, PM_V4RZRW5GWCKUEWH35RKDMDPRNXI.PHONE, PM_V4RZRW5GWCKUEWH35RKDMDPRNXI.EMAIL FROM PM_V4RZRW5GWCKUEWH35RKDMDPRNXI WHERE (PM_V4RZRW5GWCKUEWH35RKDMDPRNXI.POSTAL_CODE = 94117)