Informatica Data Quality
- Informatica Data Quality 10.5.2
- All Products

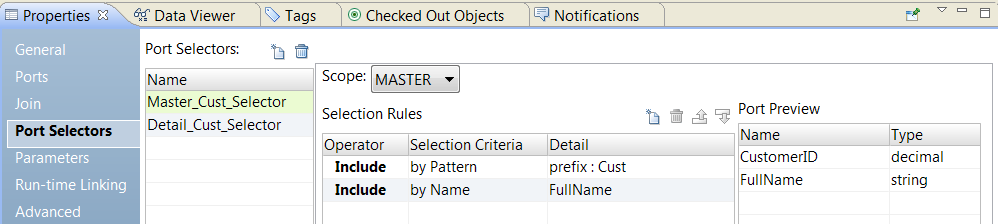
Selection Criteria
| Description
| Detail
|
|---|---|---|
All
| Includes all ports.
| No details required.
|
Name
| Filters ports based on the port name.
| Select the port names from a list of values or use a parameter of type Port or Port List.
|
Type
| Filters ports based on the data type of each port.
| Select data types from a list.
|
Pattern
| Filters ports by a string of characters in the name or by a regular expression.
| Choose prefix, suffix, or regular expression as the pattern type for the port name. Then, enter a value for the pattern or use a parameter of type String.
|