B2B Data Transformation
- B2B Data Transformation 10.4.0
- All Products

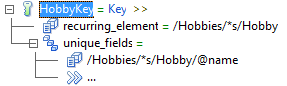
<Hobbies> <Hobby name="Swimming"> <Person firstName="Eric" lastName="Smith"/> <Person firstName="Edward" lastName="Doe"/> </Hobby> <Hobby name="Biking"> <Person firstName="Elizabeth" lastName="Doe"/> </Hobby> <Hobby name="Painting"> <Person firstName="Mary" lastName="Smith"/> </Hobby> </Hobbies>