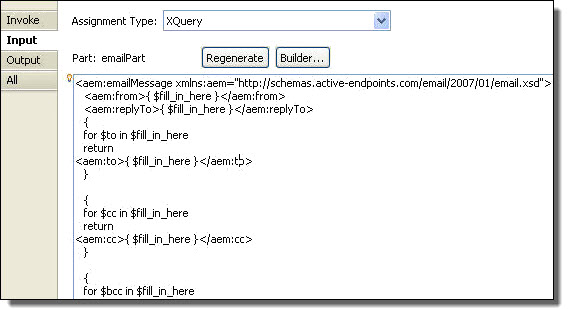
If you select the XQuery expression language, you can use the many functions that are supported by XQuery in addition to all XPath expression building. The additional XQuery function categories include Date, QName, Misc, and Constructor.
You can then create expressions for the document, as the following example shows:
Note the syntax used to generate the contents of an element, such as the following from the example above:
<aem:replyTo>{$runtimeParameters/param:emailAddress/text()}</aem:replyTo>
You must add the
text()
function to the end of the path. Any time an XQuery expression results in an element, you must add
text()
to get the contents of the element.
The path without
/text()
would result in the following:
<aem:replyTo>
<emailAddress>reply@example.org</emailAddress>
</aem:replyTo>
instead of the desired result:
<aem:replyTo>reply@example.org</aem:replyTo>
If the expression contains just a simple value and not an XML element, the expression results to the contents. For example, the following expression results in a string:
Please use the Claim #: {$refNumber}