Informatica Data Quality
- Informatica Data Quality 10.4.0
- All Products

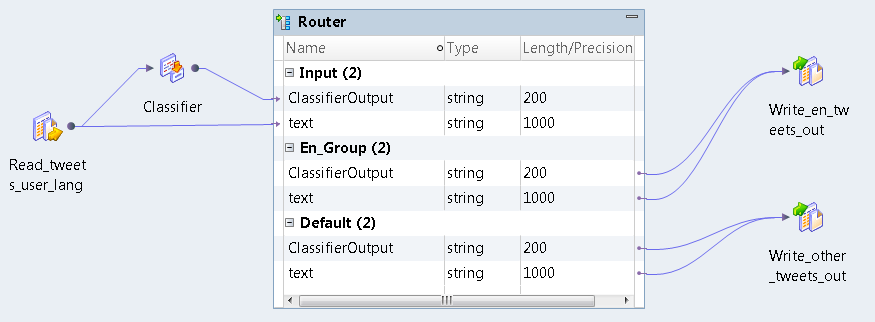
Port Name
| Port Type
| Port Group
| Precision
|
|---|---|---|---|
Classifier_Output
| Input
| Input
| 2
|
text
| Input
| Input
| 200
|
Classifier_Output
| Input
| Default
| 2
|
text
| Input
| Default
| 200
|
Classifier_Output
| Input
| En_Group
| 2
|
text
| Input
| En_Group
| 200
|
ClassifierOutput='en'