Informatica Data Quality
- Informatica Data Quality 10.4.0
- All Products

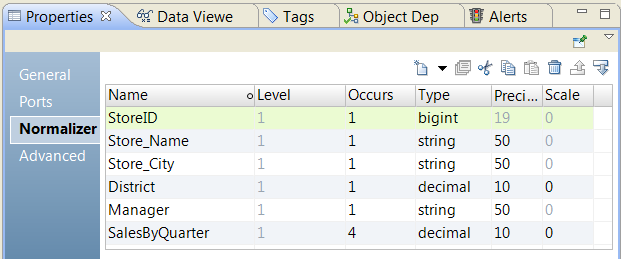
StoreID | Store_Name | Store_City | District | Manager | Quarter1 | Quarter2 | Quarter3 | Quarter4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | BigStore | New York | East | Robert | 100 | 300 | 500 | 700 |
2 | SmallStore | Phoenix
| West | Radhika | 250 | 450 | 650 | 850 |