Data Integration
- Data Integration
- All Products

|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
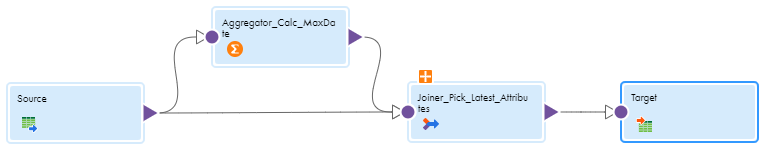
Properties
| Configuration
|
|---|---|
Incoming Fields
| Configure a field rule to prefix all incoming fields with " agg_ " so that the aggregated fields have unique names.
|
Group By
| Group by the field
agg_stock_id .
|
Aggregate
| Create one aggregate field with the following properties to return the latest trading time for each stock ID:
Configure the following expression:
max(agg_tradetime)
|
Properties
| Configuration
|
|---|---|
Incoming Fields
| Configure the following field rules:
The list of included fields shows all the source fields: PRICE, STOCK_ID, TRADETIME, VOLUME
|
Target Fields
| Add the following target fields: STOCK_ID and PRICE
|
Field Mapping
| Perform an automap with
Exact Field Name . This maps the incoming fields STOCK_ID and PRICE to the target fields STOCK_ID and PRICE.
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|